lab values for cirrhosis of the liver|Cirrhosis: Diagnosis and Management : iloilo Your doctor may recommend the following blood tests 1. liver tests NIH external link that can show if liver enzyme levels are higher or lower than normal, which may be a sign of liver damage. Your doctor may suspect . Tingnan ang higit pa Find sports betting odds for top US legal sportsbooks, including moneylines, over/unders, and spread lines. It's important to find the best odds possible.
lab values for cirrhosis of the liver,Your doctor can use blood tests to tell how serious cirrhosis is. Imaging tests. Imaging tests can show the size, shape, and texture of the liver and show how much fat is in the liver. Some tests can also measure the stiffness of the liver. Cirrhosis increases liver stiffness. Your doctor may use one or . Tingnan ang higit pa
Your doctor may recommend the following blood tests 1. liver tests NIH external link that can show if liver enzyme levels are higher or lower than normal, which may be a sign of liver damage. Your doctor may suspect . Tingnan ang higit pa
Imaging tests can show the size, shape, and texture of the liver and show how much fat is in the liver. Some tests can also . Tingnan ang higit paYour doctor may perform a liver biopsyto see how much scarring is in your liver. A liver biopsy can diagnose cirrhosis when the results of other tests are uncertain. The . Tingnan ang higit pa Laboratory tests. Your provider may order blood tests to check for signs of liver malfunction, such as high bilirubin levels or certain enzymes. To evaluate kidney .Overview. What are liver function tests? Liver function tests are blood tests that measure different substances produced by your liver. These measurements give your healthcare .

Why it's done. Liver function tests can be used to: Screen for liver infections, such as hepatitis. Monitor a disease, such as viral or alcoholic hepatitis, and determine how well .Why it's done. Liver function tests can be used to: Screen for liver infections, such as hepatitis. Monitor a disease, such as viral or alcoholic hepatitis, and determine how well . Common functions of liver include glucose, fat, protein metabolism, coagulative functions and metabolism and excretions of number of substances, immune . Liver fibrosis is scored on a scale from F0 to F4 . 23 Differentiating between significant (F2 or greater) and advanced (F3 or greater) fibrosis and cirrhosis (F4) is difficult even with.
SUMMARY. Cirrhosis can be suspected by a thorough clinical assessment, but compensated liver disease is often asymptomatic. Select investigations are .Some lab tests are done after you’ve been diagnosed with liver damage. Other tests will continue on a regular basis. These tests will monitor your health and help you and your .
Routine laboratory liver blood tests have been evaluated, as predictors of cirrhosis, but normal values of bilirubin, albumin, aspartate aminotransferase (AST), and alanine . Cirrhosis represents a late stage of progressive hepatic fibrosis characterized by distortion of the hepatic architecture and the formation of regenerative .
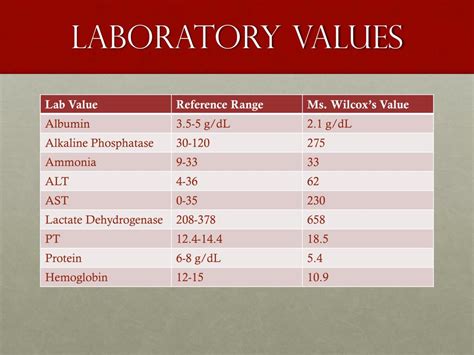
lab values for cirrhosis of the liver An AST/ALT ratio of less than one (where the ALT is significantly higher than the AST) means you may have non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.; An AST/ALT ratio equal to one (where the ALT is equal . Advanced liver disease results in a decrease in thrombopoietin production, and when cirrhosis develops, the resultant portal hypertension leads to splenic sequestration of Plts with subsequent decline in the Plt count. AST and ALT are also the most common laboratory values that clinicians check when evaluating liver function.

A related issue is the value of biochemical tests as markers of alcohol use in patients with liver disease, particularly alcoholic liver disease. Because the prognosis in alcoholic cirrhosis is greatly improved by abstinence and treatment decisions may be affected, objective and reliable measures of patients’ alcohol use can be helpful. Cirrhosis of the liver is late stage liver disease, in which healthy liver tissue has been gradually replaced with scar tissue. This is a result of long-term, chronic hepatitis. . A liver biopsy is a minor procedure to take a small tissue sample from your liver to test in a lab. A healthcare provider can usually take the sample through a . History of PBC. In 1851, Addison et al[] were the first to observe an association of skin changes with liver disease in women.Elevated serum cholesterol levels in these patients and the presence of cutaneous xanthelasmas served as a basis for employing the term “xanthomatous biliary cirrhosis” to denote this disease[11,12].Almost 100 years .
Liver blood tests are a battery of test which are easily available in biochemical laboratory and varies from hospital to hospital and country to country. 14, 15 Traditionally called as liver . Liver Tests of prognostic Value. Liver tests in patients with cirrhosis should be able to enlighten the clinician regarding the overall prognosis of .
Routine laboratory liver blood tests have been evaluated, as predictors of cirrhosis, but normal values of bilirubin, albumin, aspartate aminotransferase (AST), and alanine aminotransferase (ALT) do not exclude cirrhosis. Combinations of routine laboratory blood tests are used to predict cirrhosis, including AST/ALT ratio, AST to platelet ratio .This test may be performed to assess liver functioning and to detect liver lesions that may cause biliary obstruction, such as tumors or abscesses. Serum aminotransferases (transaminases): This enzyme is released from damaged liver cells. Prothrombin time (PTT) test: The prothrombin time test measures how long it takes for blood to clot. The model for end-stage liver disease (MELD) and Child–Pugh scores are two clinically useful calculations that use patient laboratory values and symptom severity to stratify risk and estimate disease severity in cirrhotic patients. 73 The MELD score is commonly used in transplant allocation. 74 Due to the progressive nature of chronic liver .Based on Baveno VII consensus (EASL) Persons with compensated cirrhosis without varices on screening endoscopy should have endoscopy repeated every 2 years with ongoing liver injury, overweight or alcohol use or every 3 years if liver injury is quiescent, e.g., after viral clearance, alcohol abstinence. Hepatic Venous Pressure Gradient (HVPG . Normal values are about 9.5 to 13.8 seconds. Albumin level (hypoalbuminemia): Albumin is a very common protein found in the blood with a variety of functions. It also is produced only in the liver, and if its levels are lower than normal it can be suggestive of chronic liver disease or liver cirrhosis.The most useful laboratory tests to screen for liver disorders are serum aminotransferases (the most commonly used liver tests), bilirubin, and alkaline phosphatase. Certain patterns of biochemical abnormalities help distinguish hepatocellular injury from impaired bile excretion (cholestasis—see table ).
Liver function tests are blood tests that measure different substances produced by your liver. Values that are higher or lower than normal may indicate disease. 800.223.2273; . Your technician will send your blood sample to a lab for analysis. The lab may be in the same facility or a different one. . Cirrhosis. Liver cancer. Put simply, cirrhosis is scarring of the liver. Any time an organ is injured, it tries to repair itself. And when this happens, scar tissue forms. As more scar tissue forms in the liver, it becomes harder for it to function. Cirrhosis is usually a result of liver damage from conditions such as hepatitis B or C, or chronic alcohol use.
Hepatic cirrhosis is a chronic hepatic disease characterized by diffuse destruction and fibrotic regeneration of hepatic cells. As necrotic tissue yields to fibrosis, this disease alters liver structure and normal vasculature, impairs blood and lymph flow, and ultimately causes hepatic insufficiency. The prognosis is better in noncirrhotic .
Cirrhosis: Diagnosis and Management Evaluation of Liver Function. There is a broad spectrum of laboratory tests used to evaluate liver function and liver damage. Colloquially, these are referred to as liver function tests, although they are not all direct measures of liver function. Liver testing generally includes alanine transaminase (ALT), aspartate transaminase (AST .
Therapeutic interventions and nursing actions for patients with liver cirrhosis may include: 1. Enhancing Nutritional Balance. A key aspect of managing clients with liver disease, from the stages of compensated cirrhosis through liver failure, is early recognition and treatment of malnutrition.lab values for cirrhosis of the liver Cirrhosis: Diagnosis and Management The routine tests for liver damage include complete metabolic panel (CMP) or liver panel, which include levels of bilirubin, ALT (alanine aminotransferase), AST (aspartate aminotransferase), ALP (alkaline phosphatase) and albumin. In liver cirrhosis the bilirubin level might be normal or decreased depending on the disease etiology and .
lab values for cirrhosis of the liver|Cirrhosis: Diagnosis and Management
PH0 · Value of Liver Function Tests in Cirrhosis
PH1 · Testing for cirrhosis
PH2 · Liver function tests
PH3 · Liver Function Tests: Types, Purpose & Results Interpretation
PH4 · Lab Tests
PH5 · How to Diagnose Cirrhosis
PH6 · Diagnostic tests
PH7 · Diagnosis of Cirrhosis
PH8 · Cirrhosis: Diagnosis and Management
PH9 · Cirrhosis in adults: Etiologies, clinical manifestations
PH10 · Cirrhosis